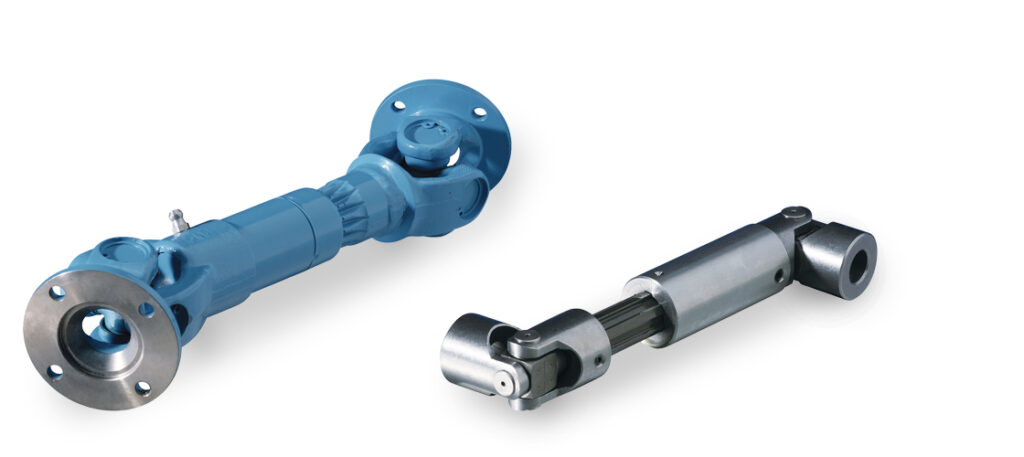
A joint shaft, also known as a drive shaft or a propeller shaft, is a mechanical component used to transmit rotational power and torque between two shafts that are not aligned with each other. Joint shafts are commonly used in various types of machinery, including vehicles, industrial equipment, and agricultural machinery.
The joint shaft consists of a series of rotating joints, also known as universal joints or Cardan joints, that allow it to transmit power and torque from one shaft to another, even when the two shafts are at different angles or positions.
The primary function of the joint shaft is to transmit power and torque between two shafts that are not aligned with each other. This allows the shafts to rotate at different angles and positions while still transmitting power and torque from one to the other.
The use of a joint shaft provides several benefits, including:
- Efficient power transmission: The joint shaft is designed to transmit power and torque efficiently, ensuring that the rotating shafts are able to transmit power to each other with minimal loss.
- Flexible positioning: The joint shaft can accommodate different angles and positions between the two shafts, allowing for greater flexibility in the design and operation of machinery.
- Reduced vibration and noise: The use of a joint shaft can help to reduce vibration and noise in the machinery, providing a more comfortable and safer working environment.
- Increased durability: The joint shaft is typically made of high-strength materials, such as steel, and is designed to withstand the stresses and forces associated with power transmission. This helps to ensure that the machinery is reliable and long-lasting.
The joint shaft is an important component in many types of machinery, and its use provides several benefits that can help to improve the performance, flexibility, and durability of the machinery.